Sleep is one of the most important building blocks for good health. The body needs that important rest to repair and recover. Without a consistent or too short night's sleep, we find it difficult to cope with everyday life, become more vulnerable to stress and even have a weakened immune system.
With that in mind, the choice of bed becomes even more important. How your body is built and what sleeping style you have affects the choice. And there is a lot to keep track of in order to find the right one in the vast range.
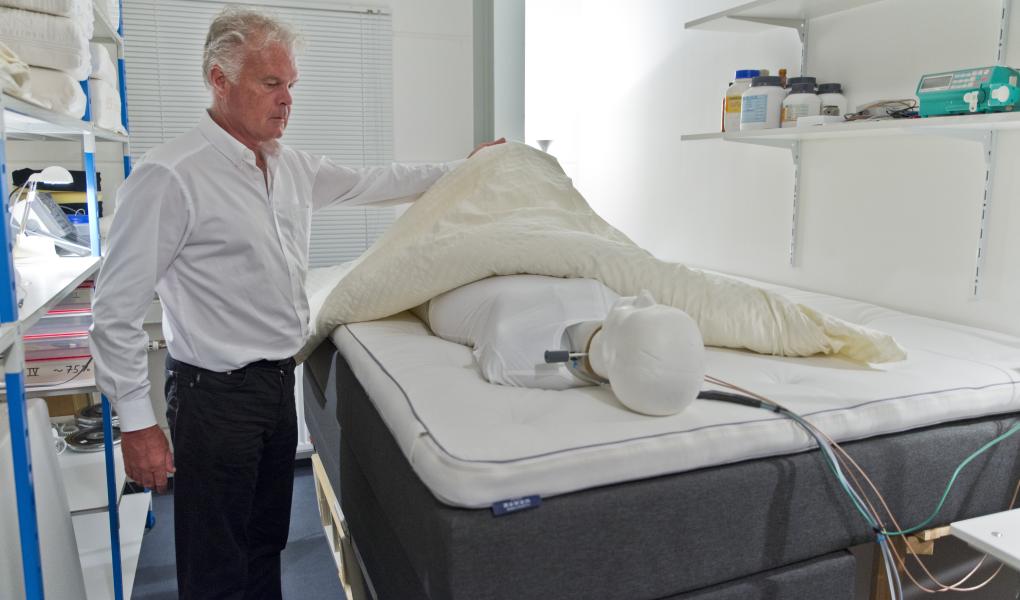
One who knows everything about ergonomics and beds is Dr. Florian Heidinger, who is head of testing at the Ergonomie Institut München. They specialize in testing and evaluating the ergonomics of everything from airplane seats to beds. Florian Heidinger and his colleagues have for several decades carried out numerous laboratory tests of beds and are considered one of Europe's foremost experts in the field.
– The body should be relaxed with the back and neck in a good position throughout the night – regardless of sleeping position, says Florian Heidinger.
The aim is for the spine and neck to remain as straight as possible. If we didn't have shoulders, everything would be much easier. They are the ones who make it happen. When we lie on our side, the shoulder pushes the body up, with a crooked back and neck as a result.
A good mattress should therefore compensate for this. It must be designed so that it gives way to the shoulder in the lateral position. The same with the shoulder blades and the butt in the supine position.
– The wider your shoulders, the more important it is that the mattress is flexible. Most mattresses take this into account and are divided into different zones.
In the zones, the springs in the mattress are structured in different ways, which means that the softness varies in the longitudinal direction of the bed.
In addition to shoulder width, weight and height should also be taken into account. The mattress must distribute the weight in such a way that it feels comfortable throughout the body, even after a long time in the same position.
The mattress should be neither too soft nor too hard. In general, you can say that someone who is tall and heavy should have a harder bed. And those who are short and light can opt for a softer one. But even a soft bed can be suitable for a heavier person, only it distributes the pressure from the body in a proportional way. Otherwise, you risk lying as if in a hammock.
The surface layer, the one closest to the body, is often the bed mattress. If the bed mattress is not soft and flexible, it can give rise to more intense pressure points on protruding body parts, such as the heels when lying on your back. A bad bed mattress can also impair the bed's ergonomic properties, by limiting the bed's ability to flex and provide support.
– Women are often more sensitive to pressure. They should choose a mattress where the surface layer has good pressure distribution, says Florian Heidinger.
It can also be good to know which position you usually lie in. It can of course be difficult to know, but the position in which you usually fall asleep and wake up is probably the one that dominates your nights.
– People who mostly lie on their backs and have narrow shoulders, for example, do not need a mattress with a very soft shoulder zone.
The next characteristic to investigate is your body temperature and whether you often overheat and sweat. This is largely controlled by the bed mattress because it is closest to the body. In general, you can say that a thicker bed mattress gets warmer and breathes worse, because you sink down more and become more enclosed.

How the mattress is structured plays a role in how hard or soft it becomes. Different manufacturers use different techniques where, for example, the coil springs have different thicknesses or are placed differently tightly. Some use springs in spring systems to regulate the pressure distribution based on the weight of different body parts.
There are mainly three bed variants on the Swedish market. Frame beds – where the mattress is made up of springs and foam resting in a wooden frame – continental beds – where two different mattresses, built in different ways, are stacked on top of each other – and freestanding mattresses which usually consist of some form of foam or latex material.
There is no clear answer as to which is preferable. Again, it all depends on how your body looks and what your needs are.
– From an ergonomic point of view, all these variants are equivalent when it comes to relief, pressure distribution and microclimate – i.e. the ability to remove heat and moisture, says Florian Heidinger.
It is simply a matter of putting them to the test. Set aside plenty of time to get a feel for it properly.
– The very best thing is to visit a store at a time when it is quiet and there are not many other customers there, says Florian.
If you can also bring someone with you, that's even better. That person can look at how your back looks in different positions. Hopefully the seller can also help and explain how each mattress is built and how it matches your body type. Preferably take off your outer clothes and shoes so that the feeling and body position are as authentic as possible.
Once you've dialed in which mattress is the best fit, it's time to focus on two other important components for the ultimate night's sleep: the comforter and the pillow. If the pillow is too flat or too thick, the angle in the neck will be wrong.
– Also keep in mind that it should work in both side and back position, says Florian Heidinger.
If the blanket is too warm, sleep becomes disturbed because it tends to go on and off throughout the night. In addition, you can suffer from muscle tension if you first sweat, take off your clothes and then get cold.
– If the bed is airy and cool, the duvet can be thicker than if the conditions are reversed.
But is there any difference between a more expensive and a cheaper bed, or is it just about brands? A more expensive bed is no guarantee that it will last longer, even cheaper beds often have good endurance today. The differences lie more in the ergonomic properties of the bed. Making a bed with more advanced suspension that provides flex and support in the right places costs more.
What you have to keep in mind is that the bed mattress is the component that is most affected over time, and which often has a large impact on comfort. During three years of use, it is exposed to 7,000 hours of pressure and moisture. This causes it to be compressed and lose its softness over time. You should therefore change the bed mattress perhaps every three years.
It is possible to find a bed that suits both you and your wallet, but it can take time. Start checking off the list and before you decide - sleep on it.
And once you're in your new bed - keep in mind that it may take a week or two for your body to get used to the new thing.



